Energy Production Costs, LCOH, LCOE
Terminology
Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE)
LCOE measures lifetime costs divided by energy production. Calculates present value of the total cost of building and operating a power plant over an assumed lifetime. Allows the comparison of different technologies (e.g., wind, solar, natural gas) of unequal life spans, project size, different capital cost, risk, return, and capacities (DOE).
Levelized Cost of Hydrogen (LCOH)
Similar to LCOE but for pure hydrogen generation. There are multiple routes to H2 other than electrolysis (using electricity) a cost calculation of the final product for each source can be useful.
Simple LCOE Concept
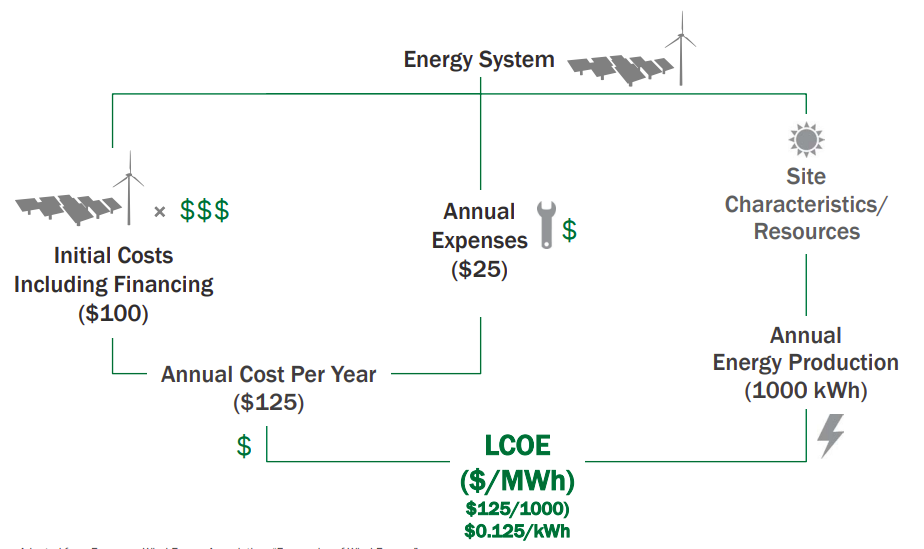
Calculating and comparing LCOE can: Measure value across the longer term, showing projected life-cycle costs.. Highlight opportunities for investors to develop different scales of projects (facility, community, or commercial).. Inform decisions to pursue projects on an economic basis, compared to utility rates.
CAPEX / Overnight cost
Overnight cost is the cost of a construction project if no interest was incurred during construction, as if the project was completed "overnight". The overnight cost is a part of the capital cost. It includes construction, system cost, procurement cost, engineering cost, cost of equipment, frst fuel load, and other costs. For quick comparisons, firms will look at what the cost of building a plant overnight would be or the overnight cost of capital. This is a hypothetical scenario because a plant cannot be constructed in one night, but it evaluates the cost of a plant if it were built right away, with current prices.
Some Data Points
-
Avi Shultz (DOE) on CSP: "Our benchmark is based on a plant of approximately 100 MW with 14 hours of thermal energy storage. We model that plant would have an LCOE of 9.5 cents/kWh (with no incentives) if built in the US today"
-
Conversion Factors, H2 has 0.143 GJ/kg
Storage
LCOH
|Source |LCOH ($/GJ) |Reference| |-------------------|------------|----------| |H2 Undergr. Salt | 1.46 |Paper | |H2 Undergr. LRC | 2.51 |Paper | |H2 Undergr. Pipes | 15.17 |Paper |
Capex and LCOE
|Source | Capex ($/KW) |LCOE ($/MWh)|Reference| |---------------------|--------------------|------------|----------| |H2 Undergr. Salt | 35 | |Paper | |H2 Undergr. LRC | 51 | |Paper | |H2 Undergr. Pipes | 386 | |Paper |
Production
LCOH
|Source |LCOH ($/GJ) |Reference| |-------------------|------------|----------| |Natgas, CCS | 13.98 |Paper | |Nuclear HTGR | 17.55 |Book | |Coal IGCC, CCS | 21.25 |IEAGHG | |PV | 26.00 |Paper | |CSP Therm + Ceria | 42.08 |Paper |
Capex and LCOE
|Source | Capex ($/KW) |LCOE ($/MWh)|Reference| |---------------------|--------------------|------------|----------| |Natgas Plant >200MW | 500 | |Paper | |Natgas Plant Typical | 1044 | |Statista | |PV Solar | 1327 | 32.78 |EIA,IEA |Gasoline | | 34.11 |Link |LOHC | 0.02 | 46.24 |Paper | |Natgas CLC | 1652 | 55.0 |Paper,Paper | |Wind, Onshore | 1718 | 50.0 |IEA |Nuclear | 7030 | 53.4 |Paper| |Wind, Offshore | 4833 | 88.0 |EIA,IEA |Biomass | 4524 | 89.0 |EIA| |Coal Wout CCS | 4074 | 68.64 |EIA| |CSP (100 MW) | 7895 | 95.0 |EIA,DOE (see above)| |Natgas + CCS | | 112.0 |EIA,IEA |Batteries | | 121.84 | EIA | |Coal Comb CCS | | 122.7 |IEAGHG| |Coal IGCC CCS | 3819 | 151.8 |Doc,IEAGHG|